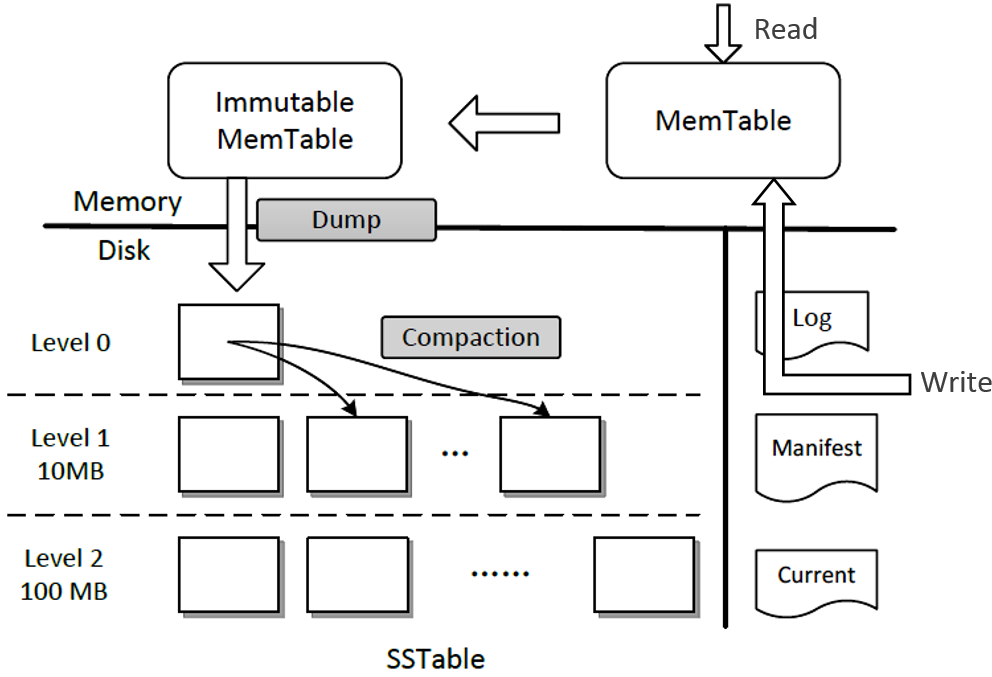
Memtable 은 log의 memory copy로 볼수 있습니다. 주요역할은 log내의 데이터를 구조화 저장하는 것입니다.
(source https://www.jianshu.com/p/0e6116f23c3d)
DB에 write를 할 때 leveldb의 kv데이터를 저장하는 공간이 Memtable입니다, Memtable에 write한 데이터가 지정한 크기(Options:write_buffer_size)를 초과하면 Immutable memtable로 변환하고 동시에 Memtable을 새로 더 만들어 데이터를 write합니다. Background에서 compaction이 일어나면 immutable을 dump to disk 해 sstable이 생성합니다.
Structure & Operation
(source https://blog.csdn.net/redfivehit/article/details/107509884)
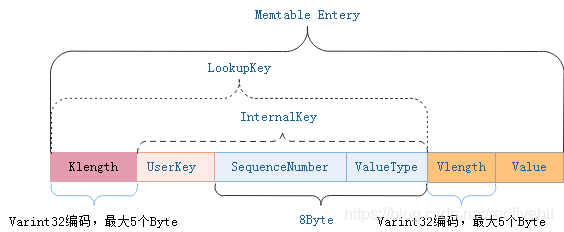
Klength&Vlength: Varint32, 최대 5Byte. SequenceNumber+ValueType: 8Byte.
- memtable key의 구성은 Leveldb:Basic Setting로 참조할수 있습니다. Memtable의 key는 4개부분으로 구성됩니다: Memtable key = key length + user key + value type + sequence number.
- Memtable에서는 같은 key의 multi version을 저장할수 있습니다. KeyComparator가 먼저 user key를 ↑순서로 비교하고, ↓순서로 sequence number를 비교하면 entry를 확정할수 있습니다. 동일한user key를 sequence number로 조작하기위해 user key를 앞에다 둔 거로 알고 있습니다.
- MemTable은 메모리의 KV entry에 대한 Add 및 Get 인터페이스를 제공하지만 실제로 Delete 작업이 존재하지 않습니다. 어떤 key의 value를 삭제는 memtable에서 삭제tag로 하나의 entry로 삽입합니다. 실제로 삭제는 compaction에서 실시 합니다.
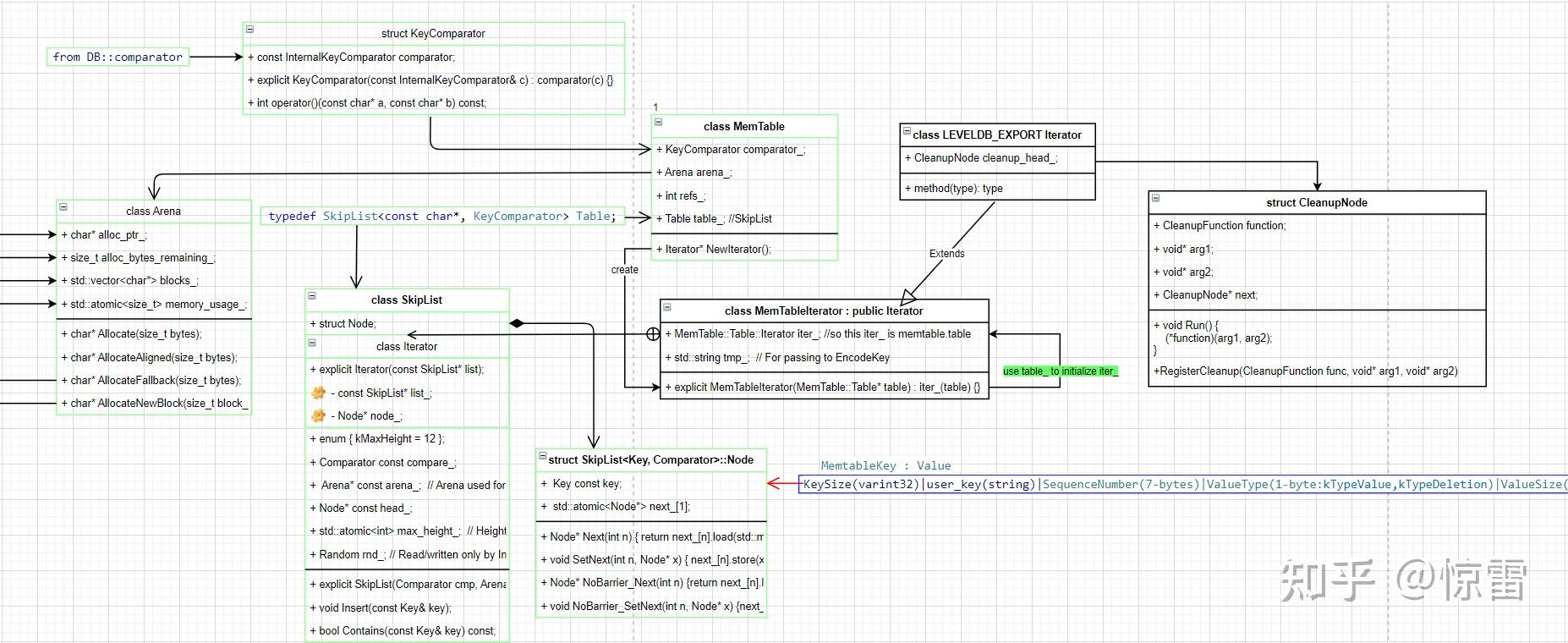
- Memtable은 interface class로 볼수 있습니다, arena와 skiplist가 베이스로 구성이 된것이 memtable입니다. 그중에 arena는 메모리를 관리하고 skiplist가 실제 kv저장에 사용됩니다.
Component
Arena : memtable의 memory관리
(source http://mingxinglai.com/cn/2013/01/leveldb-arena/)
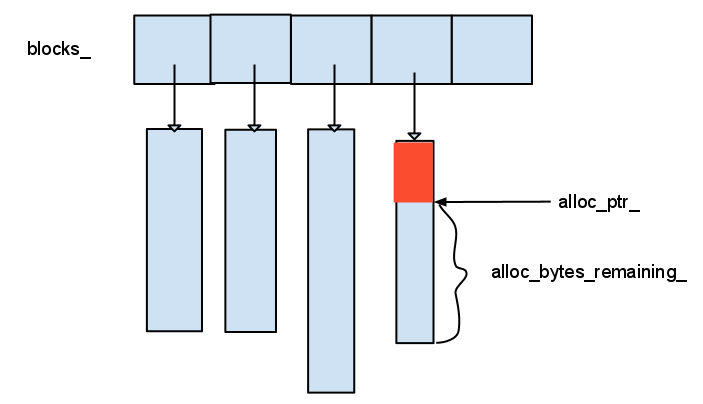
- 메모리 사용 통계를 위한 메모리 포장 작업: memtable의 크기는 한계가 정해져 있습니다(write_buffer_size), 통일한 interface로 통해 메모리를 분배.
- 메모리 정렬을 보증: Arena는 kBlockSize(static const int kBlockSize = 4096)단위로 memory를 신청, momory address정렬을 제공해서 memory의 사용을 기록하고 효율을 높입니다.(vector을 사용해서 분배한 memory를 저장)
- 빈번하게 작은 메모리 블록을 분배로 인 한 효율 낙하 과 큰 블록을 분배로 인 한 메모리 낭비를 피하기 위해: memtable이 메모리를 신청할 때 size <= kBlockSize / 4 면 현재 memory block에서 분배, 아니면 새로 신청(new) 합니다.
- Memtable의 크기가 한도에 도달하면 dump to disk를 실행, Arena가 모든 사용했던 memory를 delete/free함수 없시 삭제 합니다: memtable이 Arena를 사용하면 memtable이 disk에 dump완료후 사용했던 memory가 바로 방출되며 memory 회수를 위한 interface가 따로 필요하지 않습니다.
- Memtable에서 인용 계수(refs)가 사용됩니다: immutable_memtable이 disk에 dump완성후 삭제를 해야하지만, user가 read하고 있다면(refs != 0) 삭제를 하지 않습니다.
Skiplist : memtable의 실제 구조

(source https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list)
- 하나의 정렬 구조에 insert(random write) 조작 실행은 cost가 많아서 일반적으로 성능의 병목이 여기에 집중됩니다. List, AVL tree, B tree, skiplist등은 random write에 가속화 되어 있습니다. Leveldb에서는 복잡한 B tree를 사용하지 않고 경량한 skiplist를 사용합니다.
- Skiplist는 binary tree를 대체할수 있는 데이터 구조입니다. skiplist는 확율(node의 level을 rand함수로 설정)로 균형을 확보할수 있습니다, 구조와 실현은 binary tree보다 간단하지만 time complexity은 비슷한 O(logN)만 아니라 공간 절약도 가능합니다.
- Skiplist는 binary tree 보다 더 좋은 Concurrence성능을 가지고 있습니다: binary tree에서 업데이트를 하면 rebalancing이 발생할수 있습니다, 변경 조작은 대량node와 관련되어 대가가 높은 편입니다. .
- Leveldb의 skiplist에서 lock혹은 node refs가 필요 없습니다, Memory barrier을 통해 thread synchronization을 진행합니다:
- skiplist의 node내에 보관하는것은 InternalKey와 value로된 데이터이어서, SequenceNumber의 Globally unique 특성이 같은 node가 생성되지 않은거를 확보 할수있서 node자체가 갱신하지 않은것을 확보합니다.
- delete = put , 이어서 node의 생존주기를 기록할 필요가 없습니다.
Coding & Function Analysis
 (source https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25300086)
(source https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25300086)
Construction and destruction:
Memtable의 객체구조는 explicit call를 사용해야합니다, Arena의 초기화와 Skiplist 로 중점을 두어야 합니다. Memtable class는 Unref()로 memfree를 완성하여 leveldb에서는 copy ctor와 assignment operator를 금지합니다.
Operation:
Memtable에서 key를 찾는것은 MemTableIterator이고, MemTableIterator은 SkipList iterator 의 포장(wrapper)입니다. NewIterator은 MemTableIterator를 return하고 memtable에 저장한 데이터들을 ordered traversal에 사용됩니다.
- write : void Add(SequenceNumber seq, ValueType type, const Slice& key, const Slice& value),Status DBImpl::MakeRoomForWrite(bool force)
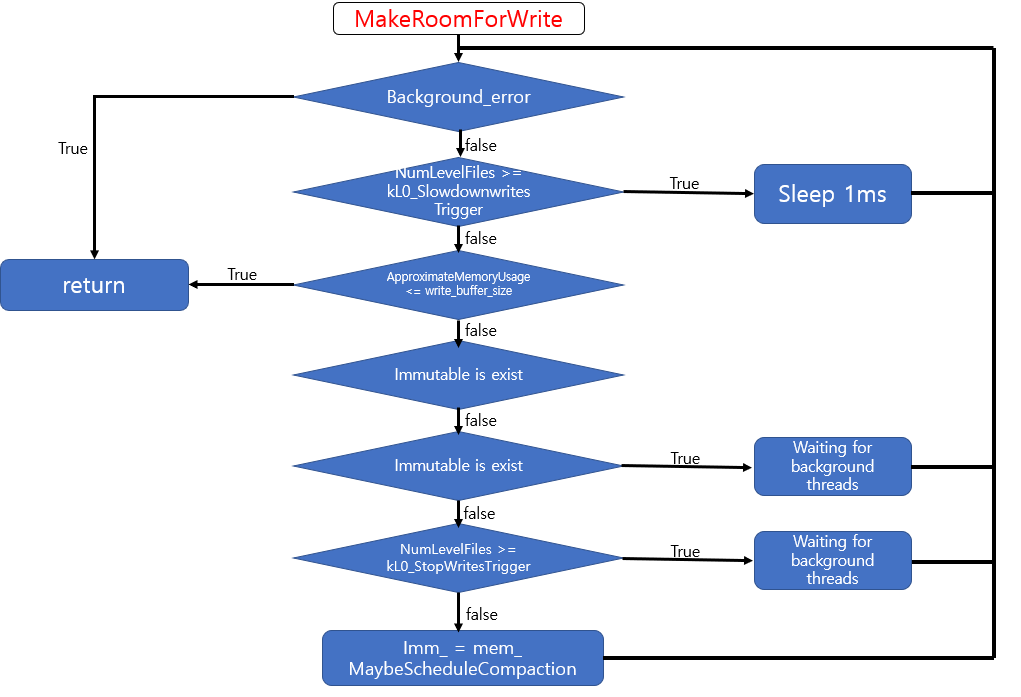
- Check level0&mem_: MakeRoomForWrite()에서 memtable,immutable,level0이 full인지 확인합니다. 만약 full이면 flush/compaction하고 새로운 memtable을 생성합니다.
- Encode: 전송된 변수를 Internalkey로 encapsulation, 이후에 value과 같이 entry로 encoding.
- Data struct에 Insert : SkipList::Insert().
- read : bool Get(const LookupKey& key, std::string* value, Status* s)
- 들어온 LookupKey에서 memtable_key를 회득.
- MemTableIterator::Seek()로 MemTableIterator를 return.
- MemTableIterator의 key를 복원 & key 의 뒷 8byte를 decoding을 통해 type를 판단.
- a) kTypeValue = 유효한 데이터, value를 return.
- b) kTypeDeletion = 무효한 데이터, Status를 NotFound로 설정.
- delete : no delete function
- ValueType = kTypeDeletion 의 entry를 add.