LevelDB에서 Get Operation을 통해 원하는 key의 value를 찾을 때, 어떤 과정을 거쳐서 key를 찾는지, 그 중에서 storage에 저장되는 SSTable에서 어떤 과정을 거쳐 찾는지에 대해 Top-Down 방식으로 알아본다.
LevelDB Get Operation
LevelDB에선 다음과 같은 순서로 원하는 key를 찾는다.
- MemTable에서 탐색
- 없다면, Immutable MemTable에서 탐색
- 없다면, storage(disk)에서 탐색
DBImpl::Get에서 다음과 같이 탐색해나가는 것을 볼 수 있다.
Status DBImpl::Get(const ReadOptions& options, const Slice& key,
std::string* value) {
// ...
MemTable* mem = mem_;
MemTable* imm = imm_;
Version* current = versions_->current();
// ...
{
mutex_.Unlock();
LookupKey lkey(key, snapshot);
// 1. Searching in the MemTable
if (mem->Get(lkey, value, &s)) {
// 2. If not in MemTable, searching in the Immutable MemTable
} else if (imm != nullptr && imm->Get(lkey, value, &s)) {
// 3. If not in Immutable MemTable, searching in storage(disk)
} else {
s = current->Get(options, lkey, value, &stats);
have_stat_update = true;
}
mutex_.Lock();
}
// ...
}
Storage에서 target key를 찾아가는 과정
즉 storage에서 target key를 찾는 과정은 Version::Get으로부터 시작하며, 다음과 같은 과정으로 target key를 찾아간다.
- 각 Level에서 target key가 있을 만한 SSTable들을 골라낸다
- 골라낸 SSTable로부터 target key를 찾는다.
Version::Get에서 다음과 같이 탐색해나가는 것을 볼 수 있다.
Status Version::Get(const ReadOptions& options, const LookupKey& k,
std::string* value, GetStats* stats) {
// ...
struct State {
// ...
static bool Match(void* arg, int level, FileMetaData* f) {
// ...
// 2. Find the target key from the selected SSTable
state->s = state->vset->table_cache_->Get(*state->options, f->number,
f->file_size, state->ikey,
&state->saver, SaveValue);
// ...
}
};
// ...
// 1. At each level, select SSTables that may have a target key
ForEachOverlapping(state.saver.user_key, state.ikey, &state, &State::Match);
return state.found ? state.s : Status::NotFound(Slice());
}
ForEachOverlapping을 호출할 때Match를 인자로 넘겨주고,ForEachOverlapping에서는 골라낸 SSTable들에 대해 인자로 받은Match를 수행해줌으로써 골라낸 SSTable로부터 target key를 찾는 과정을 수행하게 된다.
Version::ForEachOverlapping
각 Level에서 target key가 있을 만한 SSTable들을 골라낸다
- Level 0 : Level 0의 SSTable들은 key range가 겹칠 수 있다. 따라서 Linear Search로 각 SSTable들을 하나하나 판단한다
- Ohter Levels : Level 0 이외의 각 Level에선 SSTable의 key range가 분리되어 있다. 따라서 Binary Search로 target key가 있을 만한 SSTable을 빠르게 검색한다
void Version::ForEachOverlapping(Slice user_key, Slice internal_key, void* arg,
bool (*func)(void*, int, FileMetaData*)) {
const Comparator* ucmp = vset_->icmp_.user_comparator();
std::vector<FileMetaData*> tmp;
tmp.reserve(files_[0].size());
// Level 0: Picks out SSTables via Linear Search
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < files_[0].size(); i++) {
FileMetaData* f = files_[0][i];
if (ucmp->Compare(user_key, f->smallest.user_key()) >= 0 &&
ucmp->Compare(user_key, f->largest.user_key()) <= 0) {
tmp.push_back(f);
}
}
if (!tmp.empty()) {
std::sort(tmp.begin(), tmp.end(), NewestFirst);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < tmp.size(); i++) {
// Perform functions received as parameter
if (!(*func)(arg, 0, tmp[i])) return;
}
}
// Ohter Levels: Picks out SSTables via Binary Search
for (int level = 1; level < config::kNumLevels; level++) {
size_t num_files = files_[level].size();
if (num_files == 0) continue;
// FindFile : Gets index of SSTable that may have a target key via Binary search
uint32_t index = FindFile(vset_->icmp_, files_[level], internal_key);
if (index < num_files) {
FileMetaData* f = files_[level][index];
if (ucmp->Compare(user_key, f->smallest.user_key()) < 0) {
} else {
// Perform functions received as parameter
if (!(*func)(arg, level, f)) return;
}
}
}
}
골라낸 SSTable로부터 target key를 찾는 과정
TableCache::Get으로부터 시작하며, 다음과 같은 과정을 거쳐 target key를 찾는다.
- 해당 SSTable 개체가 기존에 이미 캐싱됐는지 살피고, 캐싱되지 않았다면 해당 SSTable 개체를 캐싱한다.
- 해당 SSTable 내부를 탐색해 target key를 찾는다.
TableCache::Get에서 다음과 같이 탐색해나가는 것을 볼 수 있다.
Status TableCache::Get(const ReadOptions& options, uint64_t file_number,
uint64_t file_size, const Slice& k, void* arg,
void (*handle_result)(void*, const Slice&,
const Slice&)) {
Cache::Handle* handle = nullptr;
// 1. Checks whether the corresponding SSTable has already been cached
// If not, caches the corresponding SSTable
Status s = FindTable(file_number, file_size, &handle);
if (s.ok()) {
Table* t = reinterpret_cast<TableAndFile*>(cache_->Value(handle))->table;
// 2. Find the target key via searching inside the corresponding SSTable
s = t->InternalGet(options, k, arg, handle_result);
cache_->Release(handle);
}
return s;
}
TableCache::FindTable이 수행되면서Table::Open이란 메소드가 수행되는데, 이로 인해 해당 SSTable의 Index Block과 Filter Block이 메모리로 로드된다.
SSTable 내부를 탐색해 target key를 찾는 과정
Table::InternalGet으로부터 시작하며, 다음과 같은 과정을 거쳐 target key를 찾는다.
- Index Block를 탐색해 target key가 있을 만한 Data Block을 추려낸다
- 블룸필터를 사용할 경우, 추려낸 Data Block에 target key가 있는지 블룸필터로 조사한다
- target key가 있다고 판단되면, 추려낸 Data Block에 대한 Iterator를 만든다
- 만든 Iterator를 활용해 Data Block를 탐색한다
- target key를 찾았다면 그 value를 저장한다
Table::InternalGet에서 다음과 같이 탐색해나가는 것을 볼 수 있다.
Status Table::InternalGet(const ReadOptions& options, const Slice& k, void* arg,
void (*handle_result)(void*, const Slice&,
const Slice&)) {
Status s;
// Create an Iterator for the Index Block
Iterator* iiter = rep_->index_block->NewIterator(rep_->options.comparator);
// 1. Search the Index Block and find the Data Block that may have a target key
iiter->Seek(k);
if (iiter->Valid()) {
// ...
// 2. If using a bloom filter,
// investigate with a bloom filter if there is a target key in the found Data Block
if (filter != nullptr && handle.DecodeFrom(&handle_value).ok() &&
!filter->KeyMayMatch(handle.offset(), k)) {
// Not found
} else {
// 3. If it is determined that there is a target key,
// reate an Iterator for the found Data Block
Iterator* block_iter = BlockReader(this, options, iiter->value());
// 4. Exploring the Data Block using the generated Iterator
block_iter->Seek(k);
// 5. If find the target key, save the value
if (block_iter->Valid()) {
(*handle_result)(arg, block_iter->key(), block_iter->value());
}
// ...
}
}
// ...
}
Table::BlockReader
Index Block Iterator가 가리키는 entry가 참조하는 Data Block에 대한 Iterator를 만들어 반환한다
Lookup메소드를 통해 해당하는 Data Block이 기존에 이미 캐싱됐는지 본다- 캐싱되지 않았다면 해당하는 Data Block을 캐싱한다
ReadBlock으로 해당하는 Data Block의 내용을 읽는다- 읽은 내용을 담아 새 Block객체를 만든다(즉 해당하는 Data Block을 메모리로 로드하는 것)
- 로드한 Data Block을 Cache에 넣는다
- 그 Data Block에 대한 Iterator를 만든다
만약 Cache를 쓰지 않는다면
ReadBlock으로 해당하는 Data Block의 내용을 읽고 이를 메모리로 로드만 한다
Table::BlockReader에서 다음과 같이 수행되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
Iterator* Table::BlockReader(void* arg, const ReadOptions& options,
const Slice& index_value) {
// ...
if (s.ok()) {
BlockContents contents;
if (block_cache != nullptr) {
// ...
// 1. Checks whether the corresponding Data Block has already been cached via Lookup
cache_handle = block_cache->Lookup(key);
if (cache_handle != nullptr) {
block = reinterpret_cast<Block*>(block_cache->Value(cache_handle));
} else {
// 2. If not, caches the corresponding Data Block
// 2-1. Read the contents of the corresponding Data Block via ReadBlock
s = ReadBlock(table->rep_->file, options, handle, &contents);
if (s.ok()) {
// 2-2. Create a new Block object with read contents
// (It means loading the corresponding Data Block into memory)
block = new Block(contents);
if (contents.cachable && options.fill_cache) {
// 2-3. Insert Loaded data block into cache
cache_handle = block_cache->Insert(key, block, block->size(),
&DeleteCachedBlock);
}
}
}
} else {
// If do not use cache, just load the corresponding Data Block into memory
s = ReadBlock(table->rep_->file, options, handle, &contents);
if (s.ok()) {
block = new Block(contents);
}
}
}
// 3. Create an Iterator for that Data Block
Iterator* iter;
if (block != nullptr) {
iter = block->NewIterator(table->rep_->options.comparator);
// ...
} else {
iter = NewErrorIterator(s);
}
return iter;
}
Block::Iter::Seek
Block내에서 인자로 받은 target을 찾는다
- target이 있을 만한 구역을 Binary Search로 찾는다
- Linear Search로 찾은 구역 내에서 target을 찾는다
Block::Iter::Seek에서 다음과 같이 탐색하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
void Seek(const Slice& target) override {
// ...
// 1. Find the area where the target is located via Binary Search
while (left < right) {
uint32_t mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
uint32_t region_offset = GetRestartPoint(mid);
// ...
Slice mid_key(key_ptr, non_shared);
if (Compare(mid_key, target) < 0) {
// if "mid" < "target"
left = mid;
} else {
// if "mid" >= "target"
right = mid - 1;
}
}
// ...
// 2. Find the target in the correspond area via Linear Search
while (true) {
if (!ParseNextKey()) {
return;
}
if (Compare(key_, target) >= 0) {
return;
}
}
}
기술한 내용을 토대로 SSTable내부를 탐색해 target key를 찾는 과정을 좀 더 구체적으로 다시 설명하자면 다음과 같다.
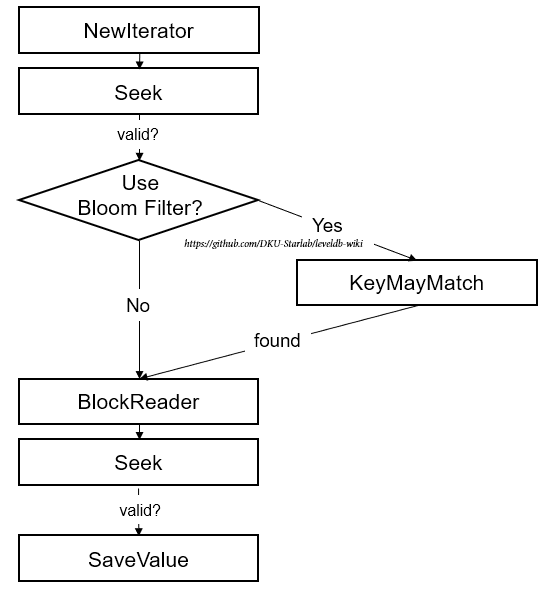
NewIterator: Index Block에 대한 Iterator를 만든다Seek: 생성한 Iterator를 이용해 Index Block내부를 뒤져 target key가 존재할 만한 Data Block를 파악한다KeyMayMatch: (만약 블룸필터를 쓴다면)블룸필터를 이용해 target key가 해당 Data Block에 있는지 조사한다BlockReader: 있다면, 해당 Data Block에 대한 Iterator를 만든다Seek: 생성한 Iterator를 이용해 해당 Data Block내부를 뒤져 target key를 찾는다.SaveValue: target key를 찾았다면 value를 저장한다.
Summary – Storage에서 target key를 찾아가는 과정 요약
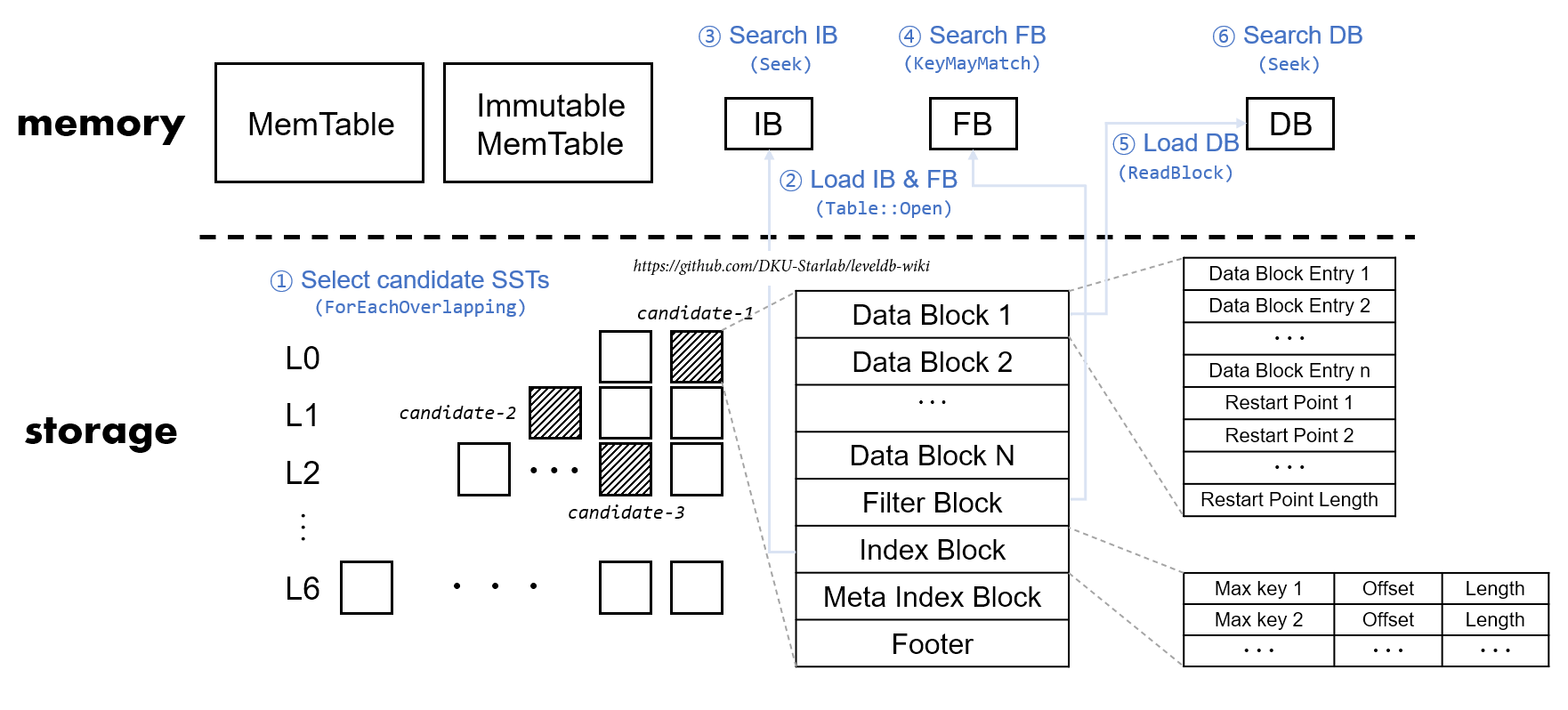
- 각 Level에서 target key가 있을 만한 SSTable들을 고른다
- 고른 각각의 SSTable 개체들이 이미 캐싱됐는지 보고 안 됐다면 캐싱해준다
- 이 과정에서 해당 SSTable의 Index Block과 Filter Block이 메모리로 로드된다
- Index Block을 뒤져 target key가 있을 만한 Data Block을 파악한다
- Filter Block의 블룸필터를 이용해 해당 Data Block에 target key가 있는지 조사한다
- 있다면, 해당 Data Block이 이미 캐싱됐는지 보고 안 됐다면 캐싱해준다
- 이 과정에서 해당 Data Block이 메모리로 로드된다
- 해당 Data Block을 뒤져 target key를 찾는다